
A risk can be described as the possibility of a threat taking advantage of a specific vulnerability in business systems which triggers a negative impact on the organization’s commercial objectives.
Using risk assessment techniques, organizations spot operational segments where the concentration of risk to activities is beyond the enterprise’s resiliency threshold.
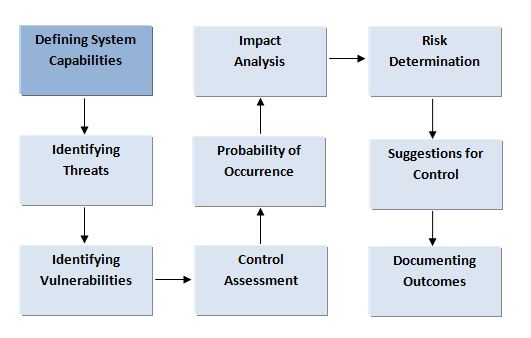
Defining System Capabilities
Describing in detail what business IT systems can and cannot do allows organizations to define their business systems capabilities within finite boundaries. This makes it easier to establish the scope of the risk assessment exercise.
Components that Comprise Business Systems
- Hardware
- Software
- Internal and External Networks
- Databases
- Personnel
- Functions of the System
- How crucial systems and their data are to the organization’s business objectives
- Level of Confidentiality
Additional factors include:
- Technical prerequisites
- IT support personnel and end users
- Security policies in line with organization resiliency objectives, compliance and statutory norms, best practices
- Network architecture
- Data protection
- Information flow through business systems
- Additional security features that include user identification, authentication, access control, encryption
- Framework for operations
- Staffing
- Maintenance
- Off location storage
- User privileges
- Environmental Conditions
- Utilities such as water, electricity and fuel
If the IT system is currently being developed, the above information can usually be obtained from design document or requirements manual. The organization’s resiliency objectives must be incorporated into the IT system while it is still under construction.
In the case of IT systems that are currently in use, the above information can be obtained from live environments, including:
- System Configurations
- Network Infrastructure
- Technical Documents
Data Collection
Some Commonly used data collection options have been listed below:
Questionnaires
Benefits
- Economical
- Practical
- Can target specific focus areas
- Time Efficient
- Can be used to obtain information from large number of people
- Data Collected from questionnaires can be easily collated, processed, interpreted and visualized to provide insights
- Participants can keep their identity confidential
- can cover a wide range of topics
Limitations
- Lack of reliability owing to bias
- Questions can be interpreted differently by different participants, leading to inconsistent data
- Cannot provide customized information
Interviews
Questions during one-on-one sessions should be framed depending on where the IT system is positioned in the software development lifecycle (SDLC).
Some stock questions have been provided below:
- How is user validity establised ?
- What are the goals and objectives of the user’s corporation?
- How do the IT systems support these goals and objectives?
- What are the technical requirements for preventing outages, reducing downtime and facilitating high availability ?
- What are the user’s corporation’s inbound and outbound information requirement ?
- Describe the information that the IT systems
- Access
- Use
- Process
- Store
- Produce
- Emit
- What is the mission criticality of the IT systems information?
- What are the channels through which system information is transmitted?
- Which division of business operations does the information cater to?
- Accounts
- Human Resources
- R&D
- Facilities
- To what extent has data confidentiality been calibrated?
- What are the different storage options that are available?
- What are the implications if personnel without valid authorization gain access to confidential data?
- How can system information access be facilitated?
- What are the implications on the corporation’s commercial objectives if data reliability is compromised?
- What is the maximum tolerable system downtime? Are these timeframes compatible with the time required to restore the systems? What are the workaround options at the user’s disposal?
- Are there any health and safety hazards that can arise due to a system failure, error, malfunction or outage?
Reviewing Avaliable Documentation on
- Policies and Procedures
- Legally binding obligations
- Systems
- User Guides
- Manuals
- User Release Notes
- Design
- Security
- Policies
- Outline
- Audits
- Test findings
- Business Impact Analysis
Automated Scanning Tools
Software applications and programs can efficiently collect information and generate customizable reports in multiple formats. The data collected includes:
- Network traffic, live ports, BIOS, configuration and so on
- Suspicious programs and behaviour on the network
- Server Configurations
- SSL issues
- Malware
- Local and external IP addresses
- Host Availability
- Asset Discovery
- Eavesdropping
- Connection Hijacking
- Suspicious Connections
See for yourself how the application works
Witness our cloud based platform’s security capabilities in action
Play around with the software and explore its features
Compare and choose a solution that’s relevant to your organization
Consult our experts and decide on a pricing mechanism
Disasters
[carousel id=’1780′ items=’4′ items_desktop=’3′ margin_right=’5′ navigation=’false’] [item img_link=”https://www.stayinbusiness.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/02/Chemical-Spills-Discharges.jpg” href=”https://www.stayinbusiness.com/resource/disaster-recovery/chemical-spills-and-discharges/”][item img_link=”https://www.stayinbusiness.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/02/Riots-Public-Disturbances.jpg” href=”https://www.stayinbusiness.com/resource/disaster-recovery/riots-and-public-disturbances/”][item img_link=”https://www.stayinbusiness.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/02/Terrorism.jpg” href=”https://www.stayinbusiness.com/resource/disaster-recovery/terrorism/”] [item img_link=”https://www.stayinbusiness.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/02/worst-product-recall.jpg” href=”https://www.stayinbusiness.com/resource/disaster-recovery/product-recall/”] [/carousel]
