Ransomware Recovery: Rebuilding and Securing your Business After a Ransomware Attack

Imagine a scenario wherein an attacker may initially utilize phishing emails or other social engineering techniques to get an entry in the target’s network, thereby using that access to install ransomware. They may use varied tactics to steal sensitive information from the target and continue to stay on the network to perform further attacks. Such possibilities emphasize the importance of preventing a ransomware attack in the first place. While prevention is important, companies must also be prepared to respond proactively to a ransomware attack and recover from it in a timely and effective way.
Ways to bounce back after a ransomware attack
Handling a ransomware attack can be a stress scenario, but it’s critical to follow an organized approach to get back your data quickly. Damage control steps after a ransomware attack are as follows:
1. Recognize the attack style and understand the detection techniques
When you identify the attack style, you will have a clear idea which measures need to be taken. You can use detection techniques like signature-based detection (where a sample of ransomware code is taken for comparison with known file signatures) and behavioral detection (assesses new behaviors and compares it to historical data for identifying indicators of compromise) to identify the infection earlier so that victims can take steps to avoid irreparable damage.
2. Isolate infected systems
Isolation is an important step even though only one computer is affected. Isolate the computer from endpoints and storage devices available on your network. Disable any form of connections including Wi-Fi and Bluetooth and disconnect the machine from any storage device. If various systems or subnets look infected, take the network offline from a switch-level perspective. Ensure to isolate system in a coordinated and systematic manner. If you are not able to disconnect devices from the network, switch them off to prevent further spread of ransomware. After isolating infected systems, gathering information about the attack, including the time it happened, the types of files that have been encrypted, etc. will be useful.
3. Scan for malicious activity
Use security tools including antivirus software, endpoint securing, or network intrusion detection systems to scan the infected systems for any indications of malicious activity. These tools utilize signatures and behavior-based algorithms to discover and detect malware.
4. Search for ransomware trigger files
Search any files that may have driven the ransomware attack. Ransomware trigger files can be in the form of a malicious attachment or link found in a phishing email, an infected piece of hardware, a drive-by download through an infected website, macro-enabled documents, or executable files. These files may have been transmitted through phishing emails, malicious websites, or software vulnerabilities.
5. Check other computers and servers on your network
Check other computers and servers on your network for altered data files. If you are not sure, unplug them from the network too.
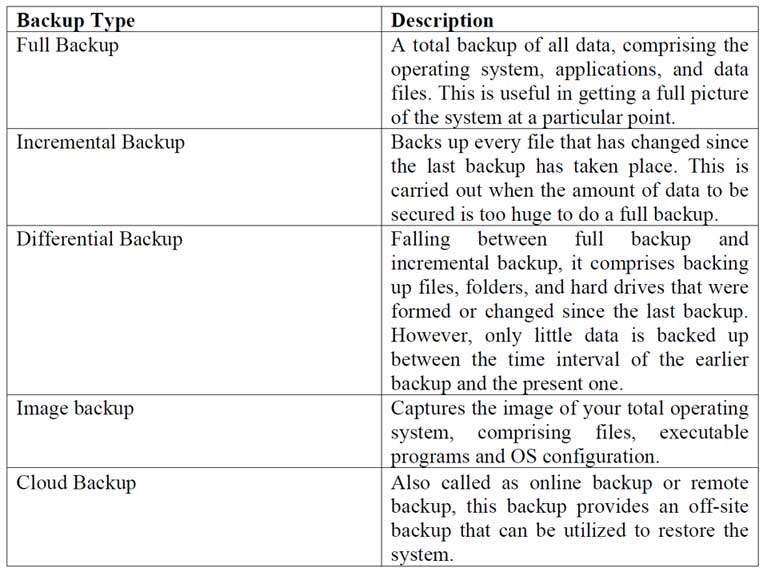
6. Perform Backup
Isolate backups to make sure they remain safe from a potential attack. The different types of backups that you can perform include:
7. Inform relevant authorities regarding the ransomware attack
The ransomware might make you think that paying the ransom amount is the only option you have. But that is not recommended. According to a recent research, 92% of organizations that paid ransom amount did not recover. Once a ransomware attack is confirmed, it is essential to inform the authorities so that they can get a good picture of who is behind the attack, how they entered your system, and what steps can be taken to halt them.
8. Restore your system
It is a good practice to either restore your system or start over completely. The best way to confirm ransomware has been eliminated from a system is by performing a total wipe of all storage devices and reinstall everything from zero. Also, formatting the hard disks in your system will make sure that there is no trace of ransomware.
9. Patch vulnerabilities
The risk of unpatched software or systems leads to the concern of ransomware increase including initial infection and compromise, operational disruption, financial losses, and ceasing of business functions.
10. Improve security
A good disaster recovery plan will have ways to recover from several data loss scenarios. Enhancing endpoint security, strengthening network security, maintaining software and systems up-to-date, monitoring for suspicious activity, etc. will help in mitigating the risk of a ransomware attack.
As per research, 60% of infosec professionals consider ransomware as serious as terrorism, only that the former is financially motivated. While prevention is key, organizations must also be well-equipped to respond to a ransomware attack thereby improving their incident response capabilities. Restoring access to data, maintaining business continuity, safeguarding reputation, maintaining compliance with regulations, and building organizational resilience attribute to the importance of recovering from a ransomware attack.
