
Vulnerabilities are faults in the system that can result from defective design, inaccurate implementation or poor maintenance. These faults can be exposed accidentally in certain operational scenarios such as:
- Deploying new infrastructure
- Revamping network design and infrastructure
- Transitioning to a cloud environment
- Introducing new or updating existing applications
- Expanding operations by adding more business centers
System vulnerabilities can also be exploited by individuals or groups with malicious intent.
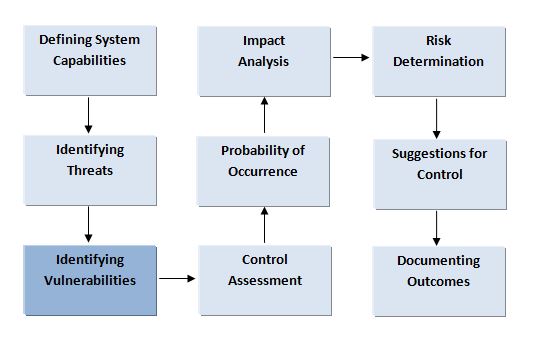
Identifying Threat Sources
Some sample vulnerability-threat-risk combinations have been detailed below:
A number of approaches can be taken to system vulnerability detection. These include:
- Regular system security maintenance
- Testing, exercises and drills based on simulated scenarios
- Creating, maintaining and updating a security checklist based on resiliency objectives
The evolutionary stage of the system as per the software development lifecycle (SDLC) determines the kind of vulnerabilities that can creep into the organization’s IT infrastructure which in turn would require the deployment of specific prevention, mitigation and restoration strategies.
- Vulnerabilities in the case of IT systems that are to be engineered in the future can be detected through the enterprise’s:
- System security guidelines
- Forecasted procedural outlines for protecting systems
- Technical Requirements
- Assessment of Security Products
- While IT systems are being installed, the scope of vulnerability detection should extend to include more specific types of inputs such as planned system security strategies as per the design document, along with the results from testing exercises.
- The vulnerabilities in IT systems that have already been installed and are currently operational can be detected through assessments of existing
- Features
- Functionalities
- Security Controls
- Technical Procedures
Technical and non-technical operational bugs and defects in business IT systems are detected through the various data collection approaches that are adopted while Outlining System Capabilities, the first stage of the risk assessment process. The online portals of suppliers also provide useful information that can be used as a foundation for questionnaires and one-on-one sessions with technical personnel. Additional material, including quick remedies, fixes and updates can also be found online.
Other documentation sources include:
- Material from Prior risk assessment exercises
- Auditory evaluations
- System anomalies
- Security revisions
- Tests, exercises and drills
- Official sources such as agencies and advisories in the government, compliance and security councils
- External associations such as provider and supplier groups
Evaluating System Security
The incidence of data breaches that result from internal causes has been steadily increasing. More than half of these incidents are unintentional, caused by a lack of attention to detail, carelessness or negligence. When highly classified information is freely sent and received across internal communication channels, the criticality of maintaining its confidentiality tends to get diluted, which in turns encourages unintentional misuse.
Automated vulnerability scanners – A group of hosts or the entire network can be inspected for assailable services through this method. However, it must be noted that many of the potential vulnerabilities detected through automated scanning are prescribed settings and configurations that are specifically recommended for the system environment. This means that some of the technical prerequisites that are necessary for the proper functioning of systems in a specific location might show up on the automation scanning tool as possible vulnerabilities.
Security test and evaluation (ST&E) – In this method, a testing framework is outlined, designed and developed which includes scripts, procedures and forecasted outputs. Loopholes in the system are detected by troubleshooting existing controls. The main purpose of the ST&E approach is to bridge the gap between existing capabilities and industry standards.
Penetration Testing – A technique in which system resiliency is inspected through simulated cyber attacks. These simulated cyber attacks can be performed in the following manners:
- No Background information on the organization’s network security systems is avaliable
- Some Background information on the organization’s network security systems is avaliable
- All the background information on the organization’s network security systems is available
- Hackers use external, public internet connections
- Hackers leverage attacks from within the company network
Penetration testing can be used to focus on specific components such as enterprise websites, servers and their corresponding software. However, penetration testing is a double edged sword and can backfire easily. If not executed precisely, complications can arise such as:
- Server Crashes
- Confidential Data Leaks
- Data Corruption
The choice or combination of choices that a company finally settles for to evaluate system security vulnerabilities depends on available budget, technology and skilled personnel.
Checklist for Security Prerequisites
This phase has to do with ensuring that the security requirements for IT systems outlined in phase 1 of the risk assessment process, Defining System Capabilities, are being met in the security controls that are currently operational or to be deployed.
Industry established security standards form the benchmark against which existing system security controls are contrasted and gaps are identified. Vulnerabilities across different segments of IT systems such as hardware, software, applications, databases, manual procedures, monitoring, management, testing and so on, can be broadly categorized into the following three dimensions.
- Managerial
- Operational
- Technical
See for yourself how the application works
Witness our cloud based platform’s security capabilities in action
Play around with the software and explore its features
Compare and choose a solution that’s relevant to your organization
Consult our experts and decide on a pricing mechanism
Disasters
[carousel id=’1780′ items=’4′ items_desktop=’3′ margin_right=’5′ navigation=’false’] [item img_link=”https://www.stayinbusiness.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/02/Chemical-Spills-Discharges.jpg” href=”https://www.stayinbusiness.com/resource/disaster-recovery/chemical-spills-and-discharges/”][item img_link=”https://www.stayinbusiness.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/02/Riots-Public-Disturbances.jpg” href=”https://www.stayinbusiness.com/resource/disaster-recovery/riots-and-public-disturbances/”][item img_link=”https://www.stayinbusiness.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/02/Terrorism.jpg” href=”https://www.stayinbusiness.com/resource/disaster-recovery/terrorism/”] [item img_link=”https://www.stayinbusiness.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/02/worst-product-recall.jpg” href=”https://www.stayinbusiness.com/resource/disaster-recovery/product-recall/”] [/carousel]
